Analysis of the force and main failure forms of jaw plates
The jaw crusher fixed jaw crushing liner produced by our company is mainly used for the rough and medium crushing of hard materials. During the working process, it bears the frictional force of the material, huge crushing force and impacts squeezing load. The working conditions are very harsh.
Force analysis
When the material to be crushed falls from a certain level of the waterfall under the action of gravity, it directly impacts the bottom material, and the movable jaw plate repeatedly squeezes and crushes the material through the reciprocating cycle motion and the fixed jaw plate. The material repeatedly rolls and slides between the movable jaw plate and the fixed jaw plate during the downward movement. Due to the material’s impact, tumble, and compression, it is subject to strong wear and tear. Therefore, the product must be able to withstand high energy multiple impact loads, and Rolling and sliding friction must have considerable abrasion resistance.
Form of failure
Wear failure
n the service process of crusher fixed jaw crushing lining, wear failure is the main form of failure. In the process of crushing the material, in addition to the impact of the material, the surface of the crushing lining of the fixed jaw is also subjected to the grinding and pressing of the material, so the wear failure modes are furrows, pits and cracks. However, due to the different materials of the lining, these three wear failure modes do not play a leading role at the same time. Tough materials with low abrasion resistance are mainly caused by furrow and deformation failure, and materials with high abrasion resistance are mainly cracks and pit failure.
Material wear is not only related to the hardness of the crushed material, but more importantly, the hardness ratio of the liner material to the crushed material. According to the basic principle of abrasive wear, the hardness Ha of the material is much greater than the hardness of the metal material Hu. , The metal material is sharply worn. When Hu / Ha > 1.25 ~ 1.30, the wear will be greatly reduced. Therefore, increasing the hardness of the material can significantly increase the material’s ability to resist abrasive wear.
Fracture failure
There are many reasons for fracture failure. First, the material itself is too low in toughness. For example, the lining material made of wear-resistant white cast iron is used in large crushers. Defects such as quenching cracks will become the source of cracks and rapidly expand under impact load. Therefore, for a lining board, if the lining board suddenly breaks due to insufficient toughness, the consequences are serious, so the lining board must have sufficient toughness.
Performance requirements of jaw crusher plates
It can be seen from the above analysis that a good crusher lining should have the following properties.
- High abrasion resistance and high hardness. According to the principle that the amount of cutting wear is inversely proportional to the hardness of the material, the hardness of the material or the hardness of a certain component in the material should exceed the hardness of the abrasive to reduce the amount of wear.
- High strength or high fatigue strength. The crusher runs continuously for 6 to 12 months, and its stress cycle can reach 6×106 ~ 6×107 times, which is already a fatigue category. High fatigue strength material prevents fatigue cracking and peeling damage.
- Some resilience. In order to prevent the lining from breaking, the material must have certain toughness. Because certain toughness is an important guarantee for its safe work.
Technical Process Analysis and Design
The jaw plate of this crusher originally used ZGMn13-4, and the mechanical properties after water toughening treatment were: σb 615 ~ 1275MPa; σ0.2 340 ~ 470MPa; ζ 15% ~ 85%; αK l96 ~ 294J / cm2; HB l80 ~ 225. ZGMn1-4 Depending on the impact load, the depth of the surface hardened layer can reach 9 ~ 18mm. High hardness hardened layer resists impact abrasive wear. Actual continuous use 15 to 20 days wear and tear failure.
Taking into account the service status of this workpiece and the advantages and disadvantages of ZGMn13-4, our company decided to use GB / T24733-2009 QTD HBW450 instead of ZGMn13-4.
Ductile Iron Jaw Plates Chemical composition design
Select low-quality S and P pig iron, use FeSi75 as an inoculant, and nebulizer FeSiMg6RE2, and add a certain amount of Cu and Mo.
- C is one of the basic elements of nodular cast iron. A suitable C content is conducive to graphitization. Because nodular graphite has the least impact on the mechanical properties of the casting, the C content of nodular cast iron is generally higher than gray cast iron. Considering that the main wall thickness of the casting is about 40 ~ 80mm, the content of C is 3.4% ~ 3.6%.
- In nodular cast iron, Si is a graphitizing element, and Si is the second most important element after C. Si can stably increase the ferrite content, effectively reduce the white tendency of the casting, and also improve the roundness of graphite. Refine the eutectic group. However, Si will increase the brittle transition temperature of the casting and reduce the impact toughness of the casting, so the Si content must be reasonably reduced, and the Si content is taken to be 2.4% to 2.6%.
- S is a typical anti-spheroidizing element. Because S has a strong affinity with spheroidizing elements such as Mg and RE, S will consume a large amount of Mg and RE in the molten iron, forming sulfides of Mg and RE, causing pores and oxidative entrapment. Defects such as slag. The sulfur content is required to be less than 0.03%.
- P is a harmful element in ductile iron. When its content is less than 0.05%, P is dissolved in the metal matrix and has little effect on the mechanical properties of the casting. When the content is greater than 0.05%, P easily segregates at the eutectic boundary, forming binary, ternary or composite phosphorus eutectics, reducing the toughness of cast iron. As the P content increases, the brittle transition temperature of the casting increases. Therefore, the content of P in ductile iron is generally required to be less than 0.045%.
- Mn in ductile iron mainly increases the stability of pearlite, easily forms carbides and affects the toughness of castings. Therefore, the lower the Mn in ductile iron, the better, but the lining plate is pearlite ductile iron, and the manganese content is 0.8% to 1.0%.
- Cu and Mo are the elements that improve the hardenability of the castings in spheroidal graphite cast iron. Cu and Mo elements are added according to the thickness of the castings to ensure that the castings can be hardened.
Ductile Iron Jaw Plates Heat Treatment
It is heated by resistance furnace and quenched by nitrate furnace.
- Austenitizing temperature and austenitizing time
The austenitizing temperature is 910 ℃ ± 10 ℃. The austenitizing time is determined according to the workpiece size, wall thickness, the number of parts that can be placed in the furnace, and the influence of the heating method. - Isothermal quenching temperature and isothermal transition time
The heat treatment converter time is less than 18 seconds, and the isothermal quenching temperature and time are determined according to the workpiece size, wall thickness, the amount of parts that the furnace can hold, the heating method, and the influence of the salt bath method. - Microstructure and properties after heat treatment
Matrix structure after heat treatment: acicular ferrite + carbon-rich austenite + graphite balls. Small amounts of martensite and carbides are allowed. Performance requirements: tensile strength δs≥1600MPa, yield strength δ0.2≥1300MPa, hardness HRC≥48, impact energy (no gap): αk≥25J.
Ductile Iron Jaw Plates Casting process design
1) Resin sand modeling. The unit weight of the casting is 183㎏, the wall thickness is uneven, and the blanking feeder is shrinking.
2) The pouring temperature is 1350 ~ 1370 ℃, the pouring time is controlled to be 29 ~ 32 seconds, and each box of molten iron is about 205㎏.
3) The casting time of each spheroidizing bag is no more than 8 minutes; the spheroidizing level is 2 or more; the graphite sphere size is 6 or more; the number of graphite spheres is greater than 100 per mm2; the spheroidizing ratio is greater than 85%; the pearlite content is greater than 50. %.
Test Results
The actual test results are as-cast spheroidization grade 2, pearlite 65%, graphite balls 5, graphite balls more than 120 per mm2, HRC51 ~ 54 after heat treatment, impact toughness 30 ~ 35J / cm2, of which acicular iron The body is smaller, see picture.
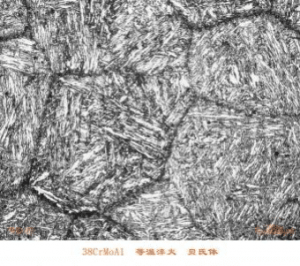
QTD HBW450 Microstructure X500 In Design Ductile Iron Jaw Plates
After being used in a 400X600 jaw crusher, the surface processing hardness can reach above HRC65. After the measurement, the thickness of the surface hardened layer is 20-25mm. After 30 days of continuous use, the teeth will show signs of wear and tear, and the teeth will be ground flat. Scrap due to 50-day wear and tear. Warmly welcomed by users.


